Using the bussola to measure angles within a circle, like Leonardo da Vinci, was eye-opening. It helped me understand how he combined art and science. This simple tool made his genius come to life for me.
The bussola was a tool used by Leonardo da Vinci to measure angles within a circle. It played an important role in his studies of geometry and shapes. Da Vinci used it to understand the relationships between angles and circles. This simple yet powerful tool has influenced modern measuring methods.
Stay tuned with us as we talk about the Bussola to measure angles within a circle, just like Leonardo da Vinci! We’ll show you how this tool helped him study shapes and how it still influences us today. Don’t miss it!
Understanding the Origins of Leonardo’s Bussola:
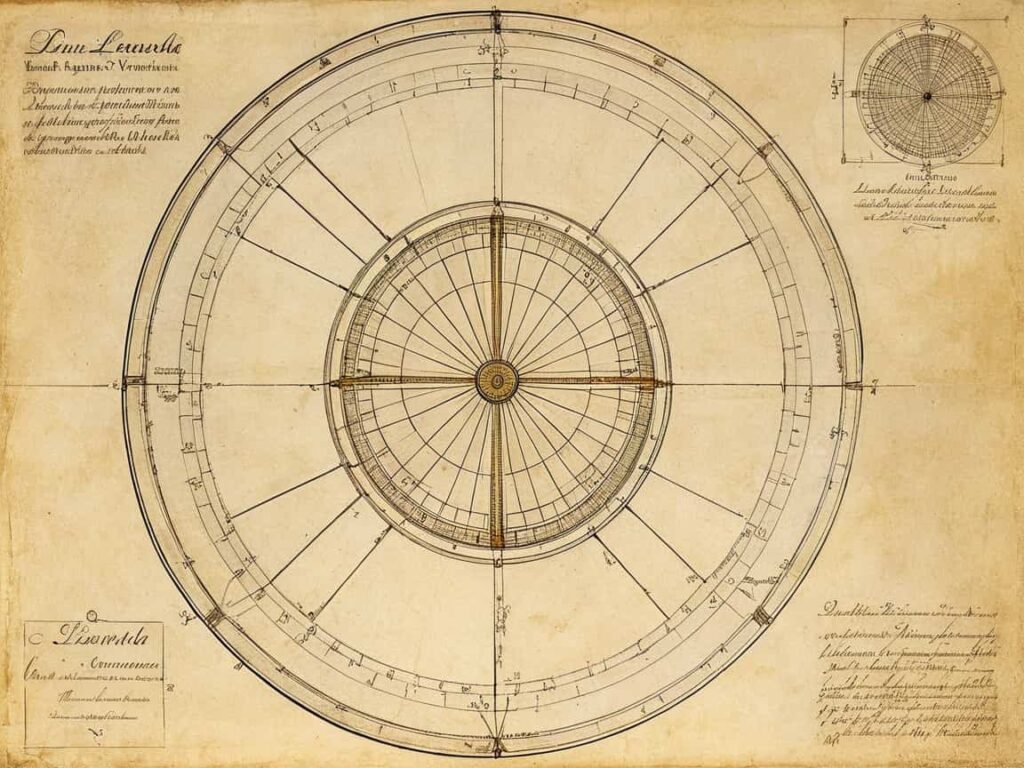
Leonardo da Vinci’s bussola was an innovative device used to measure angles within a circle. Unlike other measurement tools of its time, the bussola combined accuracy with practicality. It was designed to aid in geometric calculations, especially for artists, engineers, and architects during the Renaissance period.
Early Development and Historical Context:
In the 15th century, precise measurements were crucial in several fields. The bussola emerged as a response to the need for more accurate and reliable tools in geometry, astronomy, and engineering. Leonardo’s deep understanding of mathematics and mechanics allowed him to create a tool that could measure angles and assist in other geometric applications.
Evolution from Ancient Measuring Tools:
Before the bussola, ancient civilizations relied on rudimentary tools like the goniometer for angle measurement. Leonardo’s bussola was an evolution, making it easier to measure angles accurately and consistently. Its design reflected Renaissance advancements in scientific and mathematical thought.
Renaissance Period Influences:
During the Renaissance, there was a surge of interest in human-centered design and mathematical precision. Leonardo’s bussola was influenced by this intellectual climate, which emphasized both artistic creativity and scientific rigor. His tool was a direct product of this fusion of art and science.
The Mechanical Components of the Bussola Device:
The bussola featured a simple yet effective design, with a circular frame and a pointer to measure angles. Its mechanics were straightforward, yet the accuracy it offered set it apart from other devices of the era. The device was easy to handle and could be used to measure various angles with great precision.
Fundamental Design Principles:
The bussola was designed to measure angles within a circle precisely. The main principle behind its design was the accurate measurement of angular distances, which was critical in geometry and engineering. Its simplicity allowed it to be used across different fields.
Mathematical Precision in Measurements:
- Accuracy vs. Precision: Accuracy shows how close a measurement is to the true value, while precision shows how consistent repeated measurements are.
- Significant Figures: Use significant figures to ensure your measurements reflect their true precision level.
- Calibration: Regularly calibrate instruments to maintain precise and accurate results.
- Error Minimization: Reduce measurement errors by using proper tools, techniques, and controlled conditions.
- Standard Units: Always use standardized units (like meters, kilograms) to avoid confusion and ensure comparability.
Integration with Other Geometric Tools:
The bussola was not a standalone tool. It was often used alongside other geometric instruments, such as compasses and rulers, to aid in more complex calculations. This integration helped to advance the understanding of geometry in the Renaissance.
Leonardo’s Mathematical Vision and Geometric Studies:
Leonardo da Vinci was not just a painter; he was also fascinated by mathematics and geometry. He studied shapes, patterns, and proportions to better understand the world and improve his art. Leonardo used mathematics to create realistic and balanced works, such as “Vitruvian Man,” which shows the connection between the human body and geometry. He sketched many designs of geometric shapes and mechanical tools in his notebooks, combining art and science.
His work shows how numbers and forms are connected in nature and human creations. These studies inspired later artists, architects, and scientists, showing how important math is in creative and practical fields. Leonardo’s interest in geometry highlights his love for learning and applying knowledge in different
Applications in Renaissance Engineering and Architecture:
Structural Design Implementation
The bussola was crucial in Renaissance engineering and architecture. Architects used it to measure angles in the design of buildings and bridges, ensuring precision in structural calculations. The tool helped in creating symmetrical and balanced structures.
Military Engineering Applications
Leonardo also applied the bussola in military engineering. It was used to measure angles in the design of fortifications and siege weapons. The tool helped in calculating distances and angles for better strategic planning.
Architectural Planning Usage
In architectural planning, the bussola assisted in the creation of detailed blueprints. By measuring angles, architects could design more accurate and well-proportioned buildings, contributing to the Renaissance’s architectural masterpieces.
Role of the Bussola in Astronomical Observations:

The bussola, or magnetic compass, plays an important role in astronomical observations. It helps observers find and fix directions on Earth, which is essential for locating celestial objects in the sky. By aligning the compass with the Earth’s magnetic field, users can identify north, south, east, and west.
This makes it easier to set up telescopes or other tools to observe stars, planets, and other celestial bodies. The compass is especially helpful in areas where the horizon or landmarks are not visible, ensuring accurate positioning.
For astronomers, understanding direction is a key step in their work, and the bussola provides a simple yet reliable solution for this purpose.
Integration with Leonardo’s Artistic Endeavors:
The bussola was not just a practical tool; it also had artistic significance. Leonardo used it to measure angles in his drawings and paintings, ensuring the correct perspective and proportion in his works. The precision of the bussola was crucial in creating some of his most famous pieces.
Impact on Perspective Drawing
In his artwork, Leonardo employed the bussola to achieve accurate perspective and depth. This allowed him to create more realistic and lifelike representations, contributing to the development of modern art techniques.
Read More: Crypto30x.com ASX – Leveraging
Relationship to the Vitruvian Man
- Human Proportions: The Vitruvian Man illustrates the ideal human body proportions based on ancient Roman architect Vitruvius’ principles, highlighting symmetry and balance.
- Connection to Geometry: The drawing represents the relationship between the human body and geometric shapes, fitting within a circle and a square.
- Symbol of Harmony: It symbolizes harmony between art, science, and nature, showing how the human form reflects universal order.
- Leonardo’s Renaissance Influence: Created by Leonardo da Vinci, it reflects Renaissance ideals of blending science and art through anatomical studies.
- Cultural Icon: The Vitruvian Man is now a universal symbol of human potential and the pursuit of knowledge.
Usage in Anatomical Studies
Leonardo’s anatomical studies also relied on the bussola. By measuring angles and proportions in the human body, he was able to create accurate drawings that contributed to medical knowledge.
The Bussola’s Influence on Modern Measurement Tools:
The bussola, an early type of compass, was very important in creating modern measurement tools. It was first used for navigation, helping sailors and travelers find their way using Earth’s magnetic field. Over time, its design led to better tools like modern compasses and instruments used in navigation and mapping. The bussola’s simple idea of combining magnets with marked scales made it possible to measure directions accurately.
This invention also helped in fields like engineering, mapping, and science. Today’s advanced tools, like GPS and digital compasses, are based on the same basic idea as the bussola. It not only made travel easier but also showed how a simple tool could inspire new technologies for measuring and understanding the world.
Connection to Leonardo’s Other Inventions – You Didn’t Know About!
Leonardo da Vinci is famous for his amazing art, but he was also an inventor. He created designs for many things, including machines, tools, and even flying devices. His inventions show how creative and smart he was. For example, he designed early ideas for helicopters, tanks, and bridges.
These inventions were far ahead of his time and inspired modern engineering. By studying his work, we learn how he used science and art together.
The Bussola’s Role in Scientific Advancement:
- Navigation Breakthrough: The bussola enabled accurate navigation by using Earth’s magnetic field, revolutionizing travel and exploration.
- Foundation for Measurement Tools: Its design inspired the development of modern compasses, gyroscopes, and other precision instruments.
- Mapping and Surveying: The bussola was key in creating accurate maps and land surveys, advancing geography and engineering.
- Scientific Exploration: Its principles were applied to study magnetism and Earth’s properties, leading to discoveries in physics.
- Modern Technology Influence: The bussola’s concepts paved the way for innovations like GPS and digital navigation systems used today.
Preservation and Modern Reconstructions:
Preservation means keeping old buildings, objects, or traditions safe so they can be enjoyed in the future. It protects things from damage or decay. Modern reconstructions are when people rebuild something from the past using new materials, often to show how it originally looked. These reconstructions help others understand history and learn about how people lived long ago. Preservation focuses on saving what is already there, while reconstruction creates a new version of something old. Both are important to maintain our connection to history and culture.
Using modern technology, reconstructions can also provide accurate and detailed representations, helping everyone appreciate the past in a way that feels real and understandable.
Read More: Error ID:60d8b044-9ec3-4eeb-8e67-
Legacy and Historical Significance:
Leonardo da Vinci’s bussola holds a significant place in history due to its unique ability to measure angles within a circle. This simple yet ingenious tool was part of his many contributions to science and engineering. Da Vinci’s work in geometry influenced future generations of engineers, artists, and mathematicians. His bussola showcased his understanding of the relationship between angles and circles, making it an important device in his studies.
It highlights how Da Vinci combined art with practical inventions, which was ahead of its time. The bussola continues to be remembered as a key tool that helped shape modern understanding of geometry and engineering.
How did the bussola contribute to Leonardo’s artistic work?
The bussola played a significant role in Leonardo da Vinci’s artistic work by helping him achieve precise perspective and proportion in his paintings and drawings. With its ability to measure angles accurately, the tool enabled Leonardo to create realistic and well-proportioned compositions, ensuring that the spatial relationships in his works were mathematically sound.
This precision was essential in his ability to depict depth and perspective, giving his art a lifelike quality. The bussola, therefore, was not only a tool for geometry and engineering but also an integral part of Leonardo’s approach to achieving the harmony between art and science.
FAQ:
What exactly was Leonardo da Vinci’s bussola?
The bussola was a tool designed by Leonardo da Vinci to measure angles within a circle, aiding in geometric and engineering calculations.
How did the bussola differ from other measurement tools of its time?
The bussola was more precise and practical than earlier measuring tools, allowing for more accurate measurements in geometry and architecture.
In what fields did Leonardo use the bussola?
Leonardo used the bussola in various fields, including architecture, engineering, astronomy, and art.
What made the bussola so innovative during the Renaissance?
Its precision, simple design, and versatility made it an innovative tool for both scientific and artistic applications.
How did Leonardo calibrate and use the bussola?
Leonardo calibrated the bussola by adjusting it to ensure accurate measurements. It was used by aligning the pointer with angles and reading from the scale.
How has the bussola influenced modern measurement tools?
The bussola influenced the development of modern instruments like protractors and compasses, setting standards for precision in geometry.
Was the bussola only a practical tool, or did it have philosophical significance?
The bussola was both a practical tool and a symbol of Leonardo’s belief in the integration of art, science, and mathematics.
Are there any existing original bussolas from Leonardo’s time?
No original bussolas from Leonardo’s time exist, but modern reconstructions help us understand the design and function of the tool.
Conclusion:
Leonardo da Vinci’s bussola was more than just a tool for measuring angles; it represented the intersection of art, science, and engineering during the Renaissance. Its influence on modern measurement techniques and its role in advancing fields like geometry, astronomy, and architecture ensure its place in history.





